Health outcomes are often affected by more than biology. They can be influenced by conditions in which people are born, grow, live and work. Understanding how biologic, clinical, economic, educational, structural and social factors relate is critical to elevate health equity for all. The CCTS connects investigators and teams to the expertise and tools to conduct rigorous research involving social determinants of health.
UAB's Geographic Information System (GIS) is a tool that assists in plotting and analyzing geographical data and is useful in decision-making processes across fields like urban planning, environmental management, and business logistics.
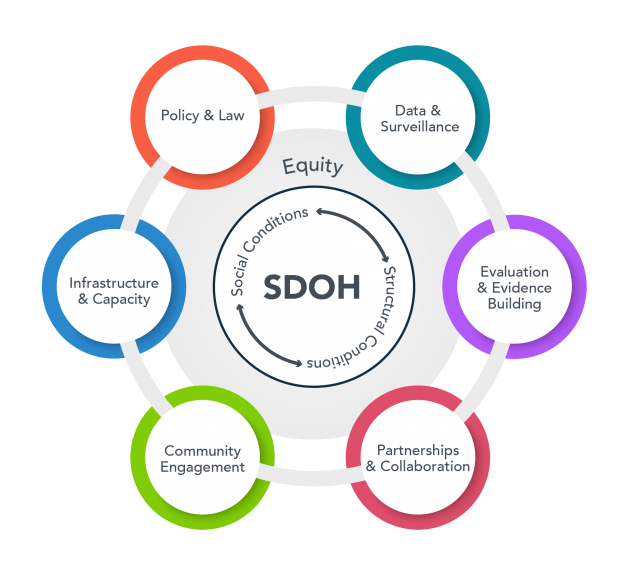
The Social Determinants of Health (SDH) Core empowers UAB investigators to evaluate how social and environmental factors influence the onset, development, management, and outcomes of diseases. It also promotes the development of interventions that mitigate these factors. By combining integrated data, methodologies, and expertise from various fields such as social science, spatial and environmental science, clinical and translational science, genomics, informatics, and epidemiology, we pave the way for pioneering investigations into the genome-sociome-exposome pathways linked to health and disease.

The CCTS’s GRID (Geospatial Research and Information Domain) provides access to tools and resources to utilize Geographic Information System (GIS) software that allows investigators to analyzes and map all types of data. Used across various industries, GIS helps in understanding patterns, relationships, and geographical contexts, thereby enhancing communication, decision-making, and efficiency. GIS offers a more dynamic understanding of the world, aiding in informed decision-making by translating complex data into a more comprehensible visual format.
